RECAP THE KEY CONCEPTS OF REPRODUCTION (FLOWERING PLANTS)
The main stages of plant reproduction are:
Pollination >>> Fertilisation >>> Formation of fruit >>> Seed dispersal >>> Germination
Male parts of the flower:
Anther (produces and stores pollen grains)
Filament (supports the anther)
Female parts of the flower:
Stigma (pollen grains land on it)
Style (supports the stigma)
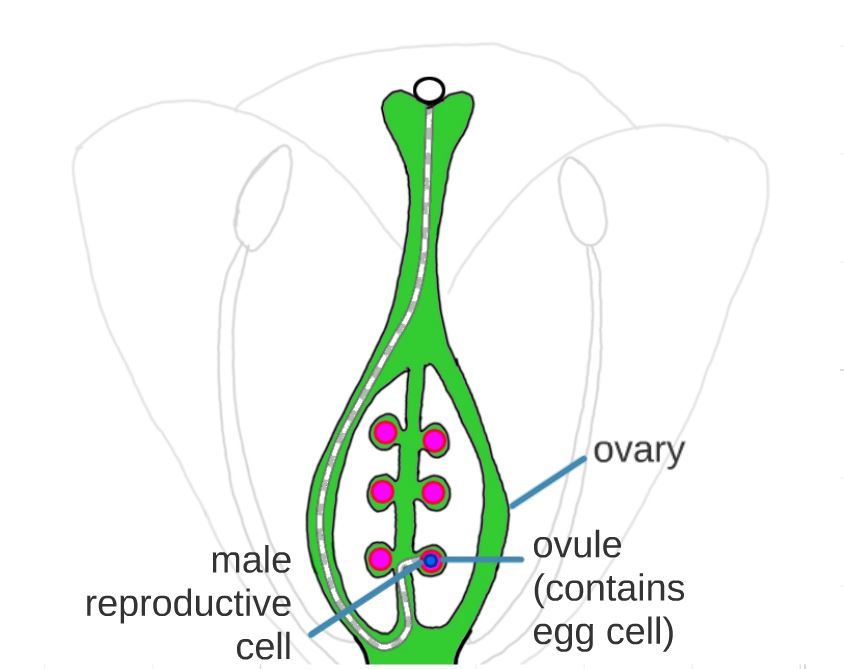
Ovary (contains ovules)
Ovule (each ovule contains an egg cell)
Pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from an anther to a stigma.
2 types of pollination:
Self-pollination (occurs within the same flower or across flowers from the same plant)
Cross-pollination (occurs across flowers from different plants)
2 methods / agents of pollination:
Pollination by animals (flowers usually contain nectar, are scented, large and colourful)
Pollination by wind (flowers are usually small and dull in colour, with stigmas and anthers hanging out of the petals)
Fertilisation
Fertilisation is the fusing of the male sex cell with the female sex cell (egg cell).
When the pollen grain lands on the stigma, it produces a pollen tube that grows down the style to the ovules in the ovary. The male sex cell travels in the pollen tube to reach the ovule in order to fuse with the egg cell.
The ovary of the flower develops into a fruit. The ovules develop into seeds.
Seed dispersal
Seed dispersal prevents overcrowding so that the young plants do not compete with parent plant for sunlight, water, space and mineral salts.
4 methods of seed dispersal: Animals, Water, Wind and Splitting
Germination
Seeds need air (oxygen), water and warmth to germinate.
The baby plant in the seed obtains its food from the seed leaves in order to germinate. The seed leaves will eventually shrivel and drop off when its food store is used up.
The seedling needs light to photosynthesise only after its first green (true) leaves have grown.
Practice: Mastering Keywords
Press submit only after selecting all the correct answers that apply.