RECAP THE CONCEPTS
Functions of various parts of plants
Plants have leaves that contain chlorophyll to trap sunlight and make food (photosynthesis).
Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and hold the plant securely to the soil.
Stems transport water, minerals and food around the plant. Stems hold leaves up so that the leaves can trap more sunlight.
Flowers develop into fruits containing seeds.
Plant transport system
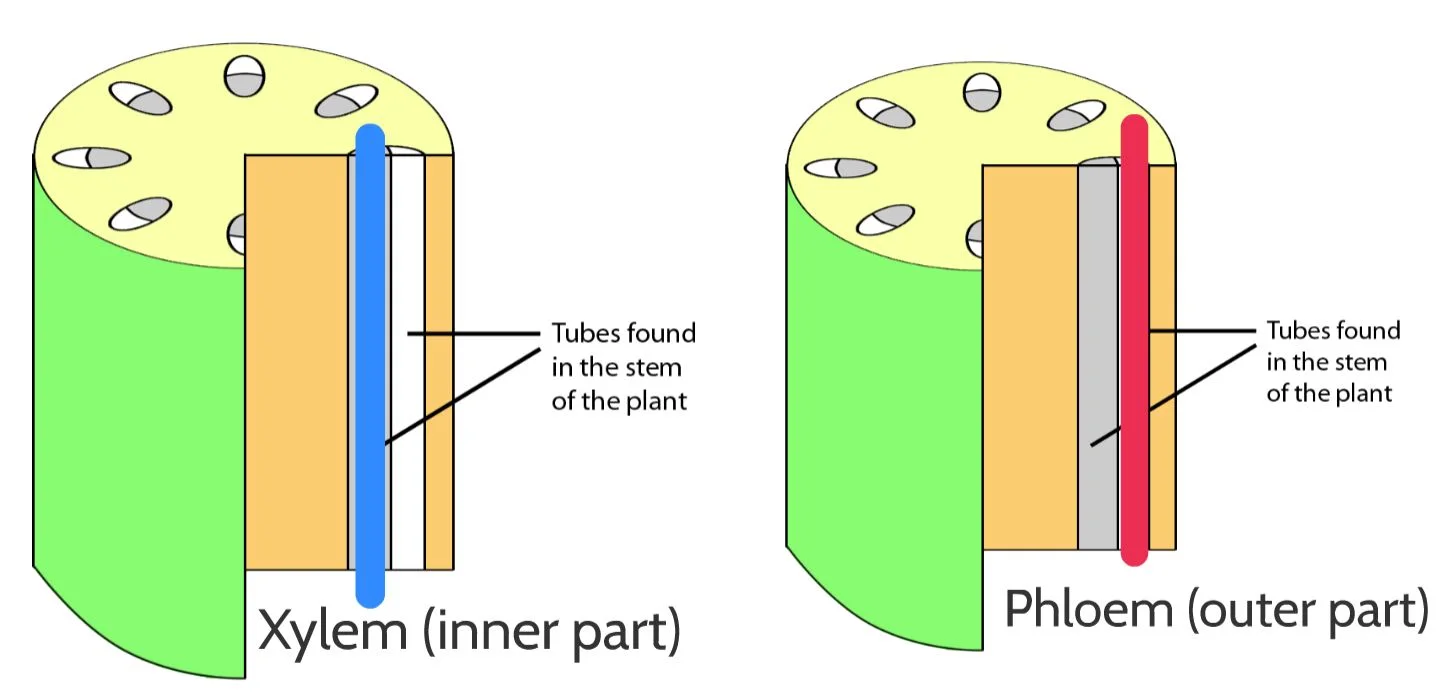
Consists of phloem (food-carrying tubes) and xylem (water-carrying tubes).
The xylem tubes transport water and minerals upwards, from the roots to all other parts of the plant.
Phloem tubes transport food mainly downwards, from the leaves to all other parts of the plant.
If a cut is made on the stem with the food-carrying tubes removed, a bulge will develop above the cut. Food from the leaves is unable to be transported to parts below the cut, such as the roots.
Plants does not transport gases. Most of the living cells of plants are located near the surface. Gaseous exchange occurs directly with the surrounding air.
Plant respiratory system
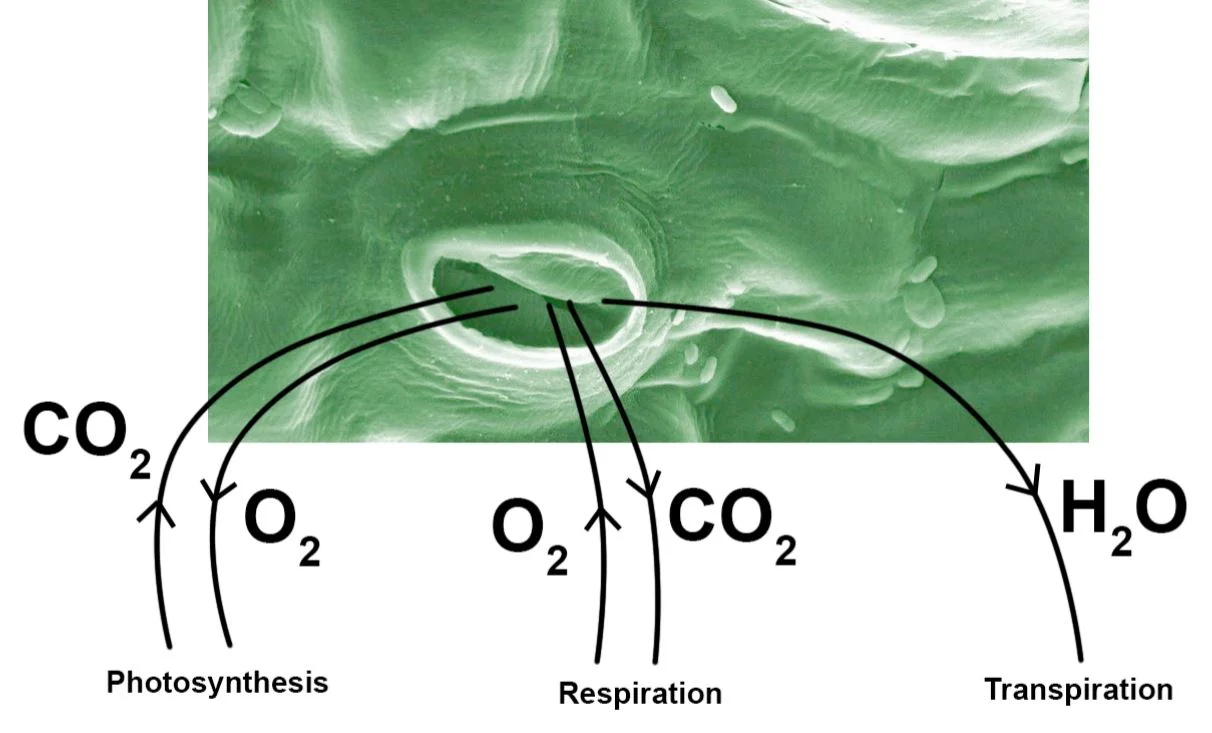
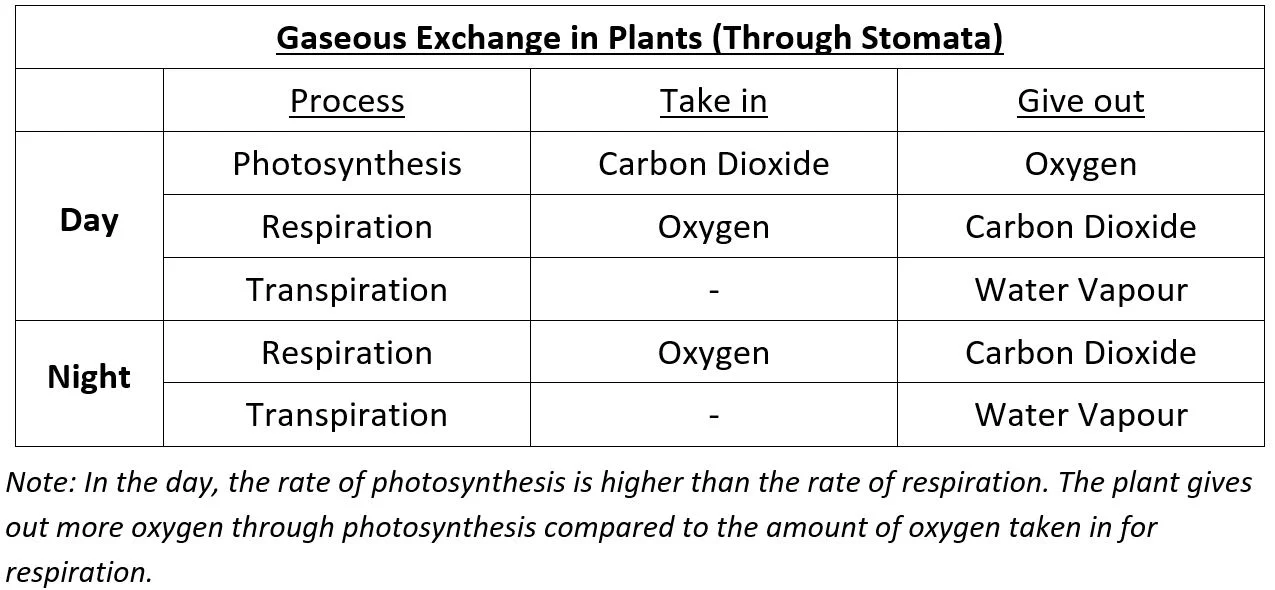
Plants exchange gases with their surroundings through stomata on the leaves.
When there is light, plants carry out photosynthesis to make their own food.
During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is taken in and oxygen is given out.Plants carry out respiration all the time in order to release energy for life processes.
Oxygen is taken in for respiration, while carbon dioxide is given out.Transpiration occurs all the time. Plants lose water as water vapour through the stomata.
Generally, the stomata are mostly found on the underside of leaves. The underside does not face the Sun directly and has a lower temperature. This lowers the rate of evaporation and reduces water loss through transpiration.
Practice: Mastering Keywords
Press submit only after selecting all the correct answers that apply.