RECAP THE CONCEPTS
Global warming
Greenhouse gases, mainly carbon dioxide, trap heat from the sun in the atmosphere. Global warming is the increase in temperature of the atmosphere due to excessive amounts of greenhouse gases.
The main cause of global warming is the burning of fossil fuels. Carbon dioxide is released when coal is burnt in power plants to produce electricity.
Deforestation also leads to global warming. There are fewer trees to take in carbon dioxide through photosynthesis.
Deforestation
Some species of living things might become extinct due to a lack of food and shelter that trees provide.
When trees are cut, there are fewer roots to hold soil particles together. Wind and rain will remove the top layer of soil which has the most nutrients. If soil erosion occurs near a water body, the topsoil is washed by rain and flows into the water.
When that happens, the water body becomes cloudy. Some sunlight is blocked from reaching fully submerged plants. This reduces photosynthesis.
Because of the increased nutrients in the water, floating plants and bacteria grow quickly. The floating plants block more sunlight from entering the water, causing fully submerged plants to die.
The increased bacteria take in dissolved oxygen from the water when they respire, causing many fish in the water to die due to the lack of oxygen.
Pollution
Haze (when forest are burnt), cigarette smoke, smoke released from factories and vehicles cause air pollution.
Plastic objects are non-biodegradable and remain for a long time in the environment. Carelessly throwing non-biodegradable materials and other rubbish causes water and land pollution.
Water pollution can be caused by chemical wastes produced by factories, fertilisers or pesticides used by farms and oil-spills.
Fertilisers used for farming can be washed into water bodies. This causes bacteria and floating plants to grow quickly.
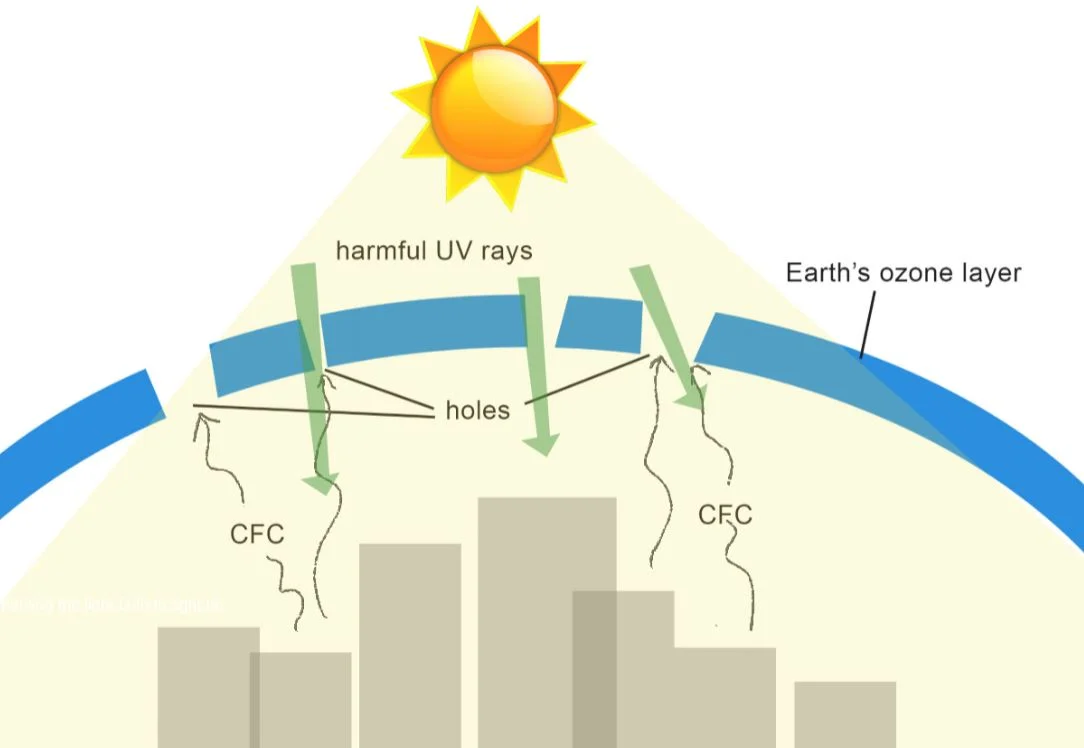
Gases known as CFCs deplete the ozone layer. This causes harmful UV rays from the sun to enter the earth’s atmosphere.
Key concepts of Habitats:
An organism is a living thing.
A population is a group of organisms of the same species that live together in a habitat.
All the different populations of organisms in a habitat form a community.
Key concepts of Food Chain and Food Web:
Only organisms (producers) with chlorophyll can trap light energy from the sun to make food.
Animals (consumers) eat other organisms.
The animal that hunts and feeds on other animals is called the predator. The animal that is hunted and eaten is called the prey. Note that herbivores are not considered predators.
Example of a food chain:
Corn plant (producer) ==> Mouse ==> Eagle (apex predator)
Food chains always start with a producer. Energy is then transferred up the food chain as one organism feeds on each another. A complete food chain should end with an apex predator. An apex predator is (usually) not a prey to other animals. It has no predators of its own.
A food web consists of interconnected food chains in a habitat.